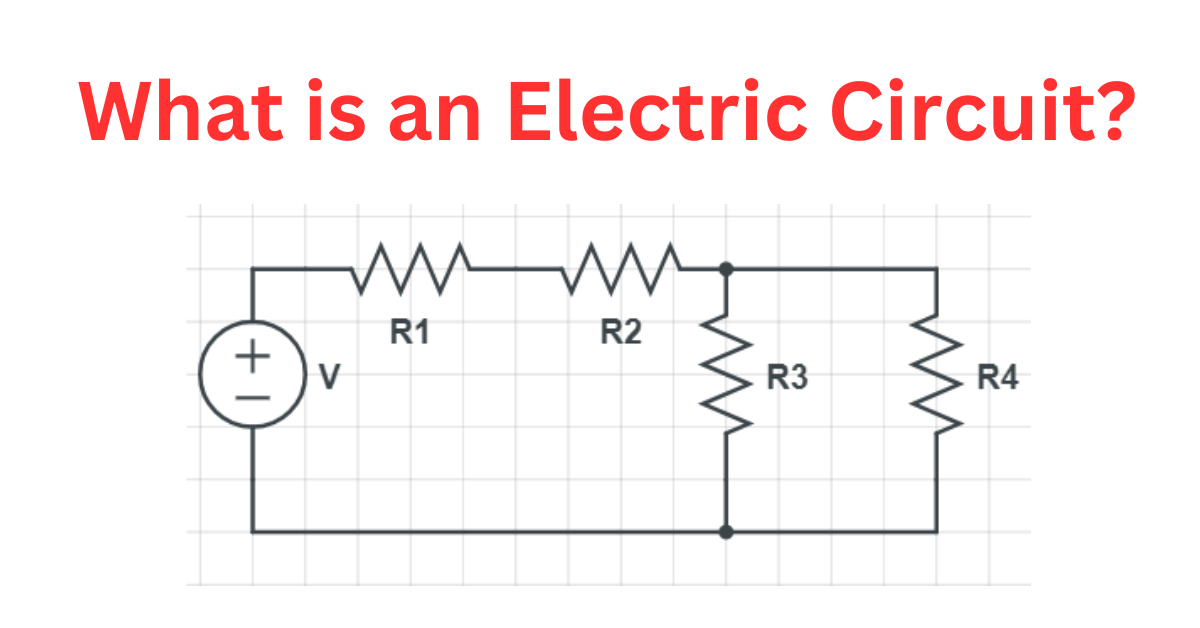
An electric circuit is a path through which electric current flows. It consists of various electrical components, including resistors, capacitors, inductors, and power sources like batteries or generators. These components are connected by conductive wires or traces, forming a closed loop that allows current to circulate.
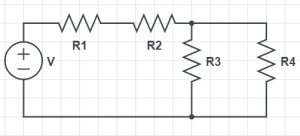
Key elements of an electric circuit include:
- Power Source: Provides the necessary voltage to drive the current through the circuit. Examples include batteries and power supplies.
- Conductors: Materials, typically wires, that allow the flow of electric current.
- Load: The component or device that consumes electrical power, such as a light bulb, motor, or resistor.
- Switch: A device that can open or close the circuit, controlling the flow of current.
- Resistors: Components that resist the flow of current, used to control the current in the circuit.
- Capacitors: Components that store and release electrical energy.
- Inductors: Components that store energy in a magnetic field when electrical current flows through them.
There are two main types of electric circuits:
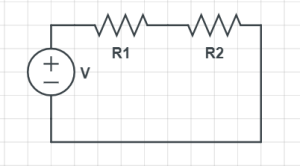
- Series Circuit: Components are connected end-to-end, so the current flows through each component sequentially. If one component fails, the entire circuit is broken.
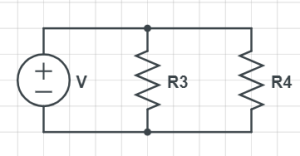
- Parallel Circuit: Components are connected across common points or junctions, creating multiple paths for the current. If one component fails, the current can still flow through other paths.
Electric circuits are used in a wide range of applications, from simple household wiring to complex electronic systems in computers and communication devices.